How long it lasts and how often the e-car battery needs to be changed
How long does the battery of an electric car last?
The battery is supposedly the weakest link in the chain of components of an electric car. Above all, the electric motor itself hardly requires any maintenance and lasts forever. It is therefore the service life of the battery that significantly determines the life expectancy of the electric car.
How long the battery of an electric car lasts depends on various variables and many details. The most important are:
- the service life of the electric car battery guaranteed by the manufacturer
- and how to handle the battery while driving and charging.
How long does the battery of an electric car last?
The details
The best and safest answer is given by the manufacturers themselves: with their warranty on the battery. With it, they guarantee that the battery retains a large part of its storage capacity, its original capacity.
- Most manufacturers currently offer a warranty of 8 years or 160,000 kilometers on the batteries of their electric cars.
- It is guaranteed that the storage capacity of the battery will retain at least 70% of its nominal capacity until then.
- For some older electric cars, the guaranteed mileage is slightly lower at 100,000 kilometers - but for some top models, some of them are significantly higher; about 240,000 kilometers for the Tesla Model S, 250,000 for the Mercedes EQS and even 1,000,000 kilometers for the Lexus UX 300e.
▶ Batteries last longer than warranty periods
The actual service life of current lithium-ion batteries significantly exceeds these warranty periods – as the research results now indicate. If you were to store a modern lithium-ion e-car battery unused at the right temperature, it would last 20 years: that's its calendar lifespan.
▶ For these reasons, e-car batteries age faster
However, the batteries age faster due to the ongoing charging and discharging – above all, the usable capacity decreases slowly but steadily. However, how quickly the storage capacity decreases can be influenced by the owner and driver:
- e.g. by a careful driving style,
- regular maintenance,
- gentle charging (no constant fast or constant emptying and full loading).
If the battery is parked for longer periods of time, it is advisable not to fully charge the battery and to store the electric car at moderate temperatures – 15 to 25 °C.
Of course, this conservation is not a must: The batteries are now so robust and the battery management system is now so good that the guaranteed service life is usually achieved without any problems, even with demanding handling. The only important thing is that the central warranty provisions are observed: otherwise, if you have a defect, you will have to pay for the repair or replacement of the battery yourself – and that is expensive.
Battery life
In everyday life, lifespan is the time between birth and death; in the case of a battery, this would be the period between production and scrapping.
In electric cars, however, the service life of the battery describes a different time frame. The battery life of BEVs is the period guaranteed by the manufacturer during which the storage capacity maintains a certain value of the initial capacity.
- The delivery of the battery or e-car marks the beginning of the period, known in technical jargon as the "Begin of Life", or "BoL" for short. The manufacturer delivers the battery with predefined characteristics, not least with a nominal capacity (kWh) and nominal voltage (400 or 800 volts).
- Every battery, every rechargeable battery, ages over time: in storage as well as through electrical use, charging and discharging. Above all, the ability to store energy decreases – capacity shrinks.
- The end of life (EoL) is reached when the storage capacity falls below a certain percentage of the nominal capacity: currently usually 70% or sometimes even 80%. In this area, the long, steady aging process begins to accelerate; albeit less strongly than feared years ago. [Autobild, VDE p. 11]
In this sense, the service life of an e-car battery is equivalent to the warranty period that the manufacturers grant on the battery.

Manufacturers currently guarantee these service lives for their electric car batteries
The battery warranty states that the usable capacity of the battery does not fall below a certain value over a promised period of time - or for a certain mileage. It applies to a brand-new e-car (first owner) and with correct use; this is laid down in the warranty conditions. The warranty or service life of the e-car battery is determined as follows:
- over the period (expressed in months or years);
- the mileage;
- and the minimum capacity after the expiry of these deadlines – expressed as a percentage of the nominal capacity.
▶ But how long does the battery of an electric car currently last at least according to the manufacturer's warranty? And which models offer the longest service life?
- The standard warranty period – and thus the standard service life of an electric car battery – is currently 8 years or 160,000 kilometres. Manufacturers such as Fiat, Citroen, BMW, Audi, VW, Opel, Mazda, Mercedes, Peugeot, Seat, Skoda and Volvo guarantee their customers that the battery will retain a usable storage capacity of at least 70% of the nominal capacity until then (as of the end of 2022).
- For some older and inexpensive electric cars, the warranty lasts for 8 years or 100,000 kilometers. Kia currently promises a battery warranty of 7 years or 150,000 kilometers for its model.
- However, some manufacturers also promise significantly longer warranty periods. At Tesla, the battery warranty for the Model S and Model X, for example, lasts. 8 years or 240,000 kilometers, for Mercedes it is 10 years or 250,000 kilometers for the EQS.
- The batteries of the Lexus UX300e currently last the longest; Toyota guarantees a service life of 10 years or 1,000,000 kilometers for the battery of its luxury brand's compact SUV.
Warranty Brand Information
| Brand | Warranty in years | Warranty in kilometers |
|---|---|---|
| Fiat | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Citroen | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| BMW | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Audi | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Volkswagen | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Opel | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Mazda | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Mercedes | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Brand | Warranty in years | Warranty in kilometers |
|---|---|---|
| Peugeot | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Seat | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Skoda | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Volvo | 8 years | 160,000 kilometers |
| Kia | 7 years | 100,000 kilometers |
| Tesla | 8 years | 240,000 kilometers |
| Mercedes | 10 years | 250,000 kilometers |
| Toyota | 10 years | 1,000,000 kilometers |
Guaranteed, actual life & the second life of a car battery
However, practical experience now indicates that the batteries last longer than expected; the guaranteed service life of a BEV battery is usually significantly exceeded in everyday use. Experts assume that current lithium-ion batteries last at least 10, but probably more like 15 to 20 years. However, there is still a lack of reliable long-term data in large numbers for a conclusive assessment. [ISI 2030, Autobild]
However, the battery's life does not have to end after use in an electric car. Its use in a second life – for example as a stationary storage system for PV systems – will become increasingly important in the future: also in order to further improve the climate and environmental impact of the electric car. The same applies to the orderly recycling of the most important raw materials.
If we succeed in establishing a sustainable battery cycle, the CO2 balance of battery-electric drives will continue to improve. The greenhouse gas balance of BEVs can be reduced from the current quarter to a third compared to diesel and petrol cars. [VDE, p.23, Focus on Roadmap, p. 18, World Economic Forum (2019)]
How the battery of an electric car works & why it ages
The fact that chemical energy can be spontaneously converted into electrical energy was discovered by the Italian physician Luigi Galvani in the 18th century. With various types of metal tools, he succeeded in stimulating the muscles of frogs' legs.
The heart of every battery, the galvanic cell, is named after Galvani. With a galvanic element, the principle discovered by Galvani is technically implemented. At its core, it consists of:
- consisting of two electrodes, a positive and a negative pole,
- and an electrolyte, i.e. a solid, liquid or polymeric chemical compound that enables the exchange of charged particles between the poles.
Modern batteries also work according to this basic principle, in which several galvanic cells are connected. In the case of the so-called primary batteries, the chemical reaction that takes place is irreversible. In the case of secondary batteries, on the other hand, it can be reversed: the battery can be recharged – we know this type of battery as accumulators, or rechargeable batteries for short.
The traction batteries in cars with a battery-electric drive (BEV for "Battery Electric Vehicle") are all secondary batteries – and now almost without exception lithium-ion batteries. The technology was developed in the 1970s and was first used commercially in a video camera. The main advantages of the lithium-ion battery are:
- the high energy and power density,
- the high cycle stability (they can be discharged and discharged very often)
- durability, robustness and safety.
The highly reactive alkali metal lithium, number 3 in the periodic table of elements, is present in all three central components or all three phases of the electrochemical reaction. Both the electrolyte and the reactive components of the electrodes contain lithium ions.
The lithium-ion batteries used in electric cars today differ primarily in the composition and shape of the electrolytes; and in the active materials used in the electrodes. The electrodes are composed of a current arrester, the collector, and a coating of active materials.
- In the negative pole, the anode, the collector is usually made of copper graphite – when the battery is charged, the lithium ions are deposited in the graphite layer.
- At the positive pole, the cathode, lithium mixed oxides are applied to an aluminum oxide – the lithium ions are deposited in the metal oxide during discharge.
The following material combinations are currently used as active materials for the cathode:
- nickel-manganese-cobalt in different concentrations (NMC);
- nickel-cobalt alumina (NCA);
- Iron phosphate (LFP) – especially in batteries from China.
Lithium-ion batteries age during storage as well as during electrical use
It is these components – the electrolyte and the active materials of the electrodes – that primarily age in a lithium-ion battery. Aging means that the electrochemical properties deteriorate, i.e. the internal resistances increase and the storage capacity decreases.
Ageing happens in the warehouse state as well as during electrical use, during loading and unloading – slowly and continuously for a long time, but then significantly accelerated at a certain point
- The ageing process in the bearing condition is referred to as the calendar lifespan,
- which is referred to as cycle stability or cycle life during loading and unloading.
In idle mode, lithium-ion batteries undergo decomposition processes on the one hand and interaction between the active materials of the electrodes and the electrolyte on the other. The extent to which these processes influence aging depends heavily on the storage conditions: the state of charge, for example, and the storage temperature. If, for example, the temperature is only 10 degrees above the nominal temperature range (usually 20 to 25°C), the calendar service life is halved.
If stored properly, experts currently estimate that modern lithium-ion batteries achieve a calendar life of around 20 years. [Source – Autobild]
Aging due to the use of the battery
However, the main reason for the aging of the battery of electric cars is the energy throughput, i.e. the continuous charging and discharging cycles. A lot of heat is generated during loading and unloading. It causes a wide variety of mechanical and chemical reactions in the battery.
- In the electrodes, for example, there are expansions and voltages, especially at the anode. They lead to changes in volume, fine cracks and deposits, such as lithium plating.
- The reserves of active lithium are decreasing with each charging cycle, while the inactive lithium is increasing.
How many charging cycles a lithium-ion battery can tolerate before the capacity drops abruptly can be influenced by cell chemistry: by the materials of the electrolytes and the active metals of the electrodes. The principle here is that the longer the cycle life, the more expensive the battery becomes.
The batteries in our smartphones and notebooks are designed for around 300 to 600 charging cycles. According to the warranty, the lithium-ion batteries in electric cars can manage at least 500 to 1,000 cycles; however, as things stand at present, they can already cope with 2,000 to 3,000 full charging cycles.
How to improve battery life
Careful, careful handling delays the aging process and extends the high-quality service life – this is no different for humans than for technical devices, including the battery of an electric car.
This means that if you handle your electric car's battery with care, it will not only last much longer than guaranteed by the manufacturer – the inevitable drop in storage capacity can also be delayed longer.
However, careful handling of the electric car battery is not a must – apart from the warranty provisions – but an option. The lithium-ion batteries of current electric cars are designed for intensive loading: designed to digest 2,000 to 3,000 full charge cycles. With a range of 300 kilometers, one would mathematically have a mileage of 600,000 to 900,000 kilometers.
However, if you save your battery, you will get more out of it for longer, especially a sustained high capacity and charging speed:
How to save the battery of your electric car
▶ Charging: When charging, you can do a lot for the well-being of the battery. Basically, it saves the battery if you avoid extremes:
- DC fast charging with high power (DC charging) should only be used when it is really necessary - and then only up to 80% of the capacity if possible.
- The charging stroke should be kept as low as possible, i.e. it is better to charge the battery from 30% to 80% instead of from 10 to 90%. Ideally, the charge level is usually between 20 and 80%.
- The car should not be parked for a long time with a fully charged battery, but should be driven immediately.
- If the battery is parked for more than half a day, it is recommended not to charge the battery more than 80%.
▶ Driving: You can also save the battery of your e-car while driving. Those who constantly accelerate at full speed put much more strain on the battery than those who drive with foresight. This driving style is exemplified by the adaptive distance assistants.
▶ The temperature: Lithium-ion batteries feel most comfortable at temperatures of 15 to 25 degrees. While driving or charging, the battery management system actively regulates the temperature via cooling or heating. This is not possible in the long run at a standstill; for longer periods of time, you should pay attention to the most moderate temperatures possible.
▶ The idle times: An electric car and its electronics work most efficiently while driving. If the e-car is parked for a longer period of time, it should be parked away from direct sunlight, cold and wet. It is also good to observe the charge level of the battery: it should ideally be between 50 and 60% of full capacity.
How often do e-car batteries have to be replaced?
As long as everything goes as planned and guaranteed, never. The first owner of an electric car can rely on the battery warranty. The majority of manufacturers guarantee that the battery will last over 70% of its initial capacity for at least 8 years or 160,000 kilometers. Individual manufacturers are now extending the guaranteed service life of the battery of their electric cars to even longer periods of time. The lithium-ion batteries of the current generation are even more durable than expected and can easily manage 2,000 full charge cycles and more.
If the storage capacity nevertheless drops more than guaranteed sooner, this is a warranty case: the battery is repaired or replaced at the manufacturer's expense.
A warranty case should be reported to the manufacturer immediately. He initiates the warranty process. The battery is repaired or replaced exclusively in the repair centres and workshops provided for this purpose.
The repair takes about one working day and costs about as much as replacing the engine of a diesel or gasoline engine: several thousand euros.
Replacing the battery is a little faster, but it is much more expensive. Depending on the manufacturer and model, the costs range between just under 7,000 and around 38,000 euros.
As with all technical components, however, e-car batteries can also malfunction; Accident damage cannot be ruled out either. That's why the rechargeable batteries of electric cars are designed in such a way that they can be repaired or completely replaced if necessary.
The possibility of replacement or repair is central, because the battery is by far the most valuable component of an electric car. The disadvantage of its high value: replacement and repair are expensive.
However, during the guaranteed service life of the electric car battery, these costs are covered by the manufacturer – provided that the warranty conditions have been met.
Battery replacement as a warranty case
You should follow these basic rules
The rules of use in the warranty conditions vary in detail from manufacturer to manufacturer. In any case, however, it is advisable to read the terms and conditions carefully – even if it has not yet been legally clarified whether they are strictly adhered to regulations or rather recommendations for action.
In order to ensure the guarantee in the event of damage, some general rules should nevertheless be observed:
- The maintenance intervals prescribed by the manufacturer must be observed.
- The manufacturer's software updates should also be installed. At Tesla, all updates provided must be installed; otherwise the warranty will be lost. For other manufacturers, this mainly applies to updates for recalls and certain service measures.
- In addition, it is advisable not to retrofit the electric car on your own - for example with a trailer hitch; the specified towing, support and roof loads must be strictly adhered to.
- Deep discharges due to long periods of inactivity should also be avoided as far as possible; however, they are only considered a reason for exclusion by some manufacturers, such as BMW.
This is what a battery replacement costs
If the defect in the battery is a warranty case, the costs of repair or replacement are covered. A case for the warranty would be, for example, if the usable capacity drops below the guaranteed minimum percentage of the nominal capacity before the end of the service life.
▶ Complete replacement of the battery
After the expiry of or out of warranty, replacing a battery is only worthwhile in the rarest of cases. The costs are high – in the case of used cars, often higher than the residual value of the e-car.
How much it costs to replace the battery is reluctant to be openly communicated by the manufacturers. The cost differences are enormous, with some car manufacturers the costs also differ depending on the cause of the damage (defect, accident).
What is certain, however, is that replacing an electric car battery is expensive: it costs at least 6,500 euros, for example for a Smart EQ or a Dacia Spring Electric. In most cases, however, the costs are in the five-digit euro range:
Mercedes estimates almost 20,000 euros for battery replacement for an EQS and even a good 27,000 euros for the electric V-Class EQV. At VW, replacing the battery costs around 10,000 to 20,000 euros. Battery changes are currently particularly expensive for a Hyundai Kona Electric: at 34,000 euros for the large battery; and for the Volvo XC40 Recharge Pure Electric with a good 38,000 euros. The replacement of the battery itself is usually quite fast. Depending on the capacity and manufacturer, it takes a few working hours to one working day.
▶ Repairing the battery
In many cases, however, the damage, such as too low a capacity, can be repaired by repair.
Repair means that one or more defective modules are replaced; possibly only a defective electrical or electronic component. At least one module is always replaced and never the smaller units of the battery, the cells. The repair is usually somewhat more time-consuming than replacing the entire battery – the entire battery housing must be removed and reinstalled, the defective module(s) must be replaced and the repaired battery must finally be technically inspected in detail. The effort is comparable to replacing a combustion engine after engine damage. On average, a repair takes one working day – the costs amount to several thousand euros, as with engine damage. In any case, repair or replacement can only be carried out by the manufacturer's authorized specialist workshops; although not all workshops are currently equipped for this. VW, for example, currently operates almost 500 bases in Germany that can repair or replace batteries. [Source – Stern, ADAC]
How are modern batteries constructed?
It cannot be ruled out with certainty that the battery of an electric car will have to be repaired or replaced. Modern lithium-ion batteries therefore have a modular design. This makes both easy for professionals.
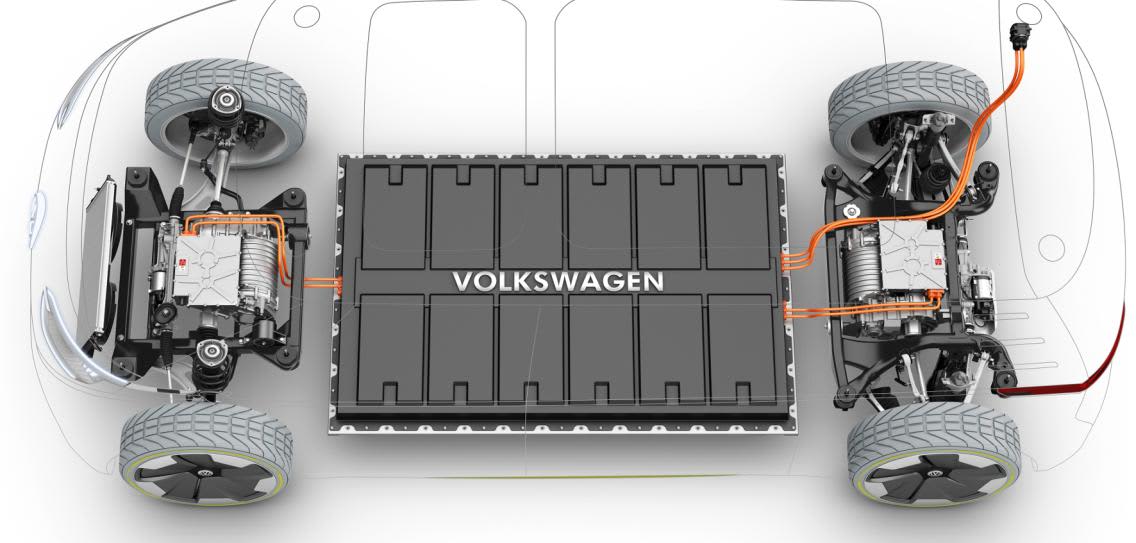
The finished battery is installed in a protective housing (steel, aluminum, carbon) as a uniform battery pack in the "skateboard" design: i.e. in the underbody of the electric car between the two axles. This ensures the highest possible safety on the one hand and the lowest possible overall centre of gravity on the other – a plus in terms of driving dynamics and road holding.
The modular design of a lithium-ion battery for electric cars means that several cells are linked to modules, and several modules are linked to form a battery:
- Several battery cells are combined into one module – usually in series. This merger is also necessary because the voltage of a single cell would be far too low to drive an electric car. The cell voltages currently range between 2.2 and 4.2 volts, depending on the cell and electrode chemistry used.
- Each module is equipped with its own cell control system.
- What the modules lack are, among other things: a protective housing and the electronic control devices.
- For this reason, depending on the size and desired range of the batteries, around a dozen modules are combined to form the battery.
Part of the finished battery is the battery management system (BMS), the control center, the brain of the individual cells and modules.
- It monitors and regulates the state of charge during loading and unloading at the level of the cells as well as at the level of the entire system.
- It compensates for slight production-related fluctuations in individual cell parameters (capacitance, voltage, internal resistance, etc.). This "balancing" function prevents individual cells from being unintentionally over-discharged or over-discharged.
- It acts as a central interface between the battery and the other electrical and electronic components of the electric drive. In doing so, it monitors and regulates the voltage, currents and temperature: of the entire battery and the individual cells.
- It allows exact logging of processes and possible errors and can thus switch off the system or individual modules in a targeted and safe manner.
In short, the battery management system guarantees the highest possible electrical safety and battery life of an electric car.
The mechanical, physical protection of the sometimes highly sensitive individual parts of the battery and the cooling system is provided by the housing of the battery. It protects the battery from stone chips, dust, water and corrosion. It is made of steel, aluminium or, in the case of particularly high lightweight construction requirements, also of carbon fibres (carbon).
Can you extend the service life as a driver?
Modern lithium-ion batteries are robust and cycle-resistant. Many experts now assume that they will outlive the cars in which they were originally installed.
The guaranteed service life of a battery in current electric cars is at least 160,000 kilometres: that is an average of around 1,000 full charging cycles (full charging and discharging). However, the experience of the last ten years and ongoing inspections show that the current battery generation can easily withstand 2,000 to 3,000 full charging cycles.
Nevertheless, it doesn't hurt not to strain or strain the battery unnecessarily: especially since it can be easily avoided. With these simple tips, you'll get more out of your battery for longer.
- An electric car with a fully charged battery should not be left standing for long – this would promote the aging process of the battery.
- Fast charging with direct current and high power puts more strain on the battery than slow charging with alternating current and little power - the latter should therefore be the rule.
- You should avoid completely discharging the battery at all costs; At the same time, you should not charge too "early", if possible at 20 to 40%. The reason: a large charging hub stresses the battery chemistry.
- Batteries feel most comfortable at outside temperatures of 10 to 25 °C and at operating temperatures between 20 and 40 °C. The operating temperature is regulated by the electronics, and if the electric car is parked for a longer period of time, you should keep an eye on the outside temperature.
Of course, as mentioned, these are only recommendations for action that do not have to be slavishly followed. The latest generation of lithium-ion traction batteries are extremely durable, intrinsically safe – and equipped with a clever management system.
If you avoid extremes, you will enjoy your battery for a long time and never have to replace the battery. [Source Autobild, VW, ADAC]
Can I replace the battery of my electric car myself?
Short answer: No. Long answer: No, absolutely not.
The manufacturers do not intend to replace the battery by the owner. It is the sole responsibility of the authorised workshops.
If you try it anyway, you lose the warranty on the life of the battery. In addition, lithium-ion batteries of today's BEVs are high-voltage batteries with voltages of 400 or 800 volts – only experts should handle such high voltages: improper handling poses a risk to life.
The trained specialists in the manufacturer's authorized repair centers and workshops are of course able to safely repair or replace a battery.
Depending on the manufacturer and size of the battery, a specialist needs a few hours to a day to replace the entire battery. The cost ranges are high, with enormous fluctuations between the brands and models: from about 7,000 to almost 40,000 euros. The repair of individual modules is somewhat more complex and therefore takes longer; however, it is significantly cheaper than complete replacement. On average, the repair of a module takes one working day – comparable to a conventional engine change. The costs are also within a similar range. Outside the service life of the electric car battery, repair is therefore usually the only financially sensible option; in the majority of cases, however, the problem can be solved.
Post a Comment for "How long it lasts and how often the e-car battery needs to be changed"